Dose Calibrator Simulated F-18 & Cu-64 (Ge-68)
Dose Calibrator Simulated F-18 & Cu-64 (Ge-68)
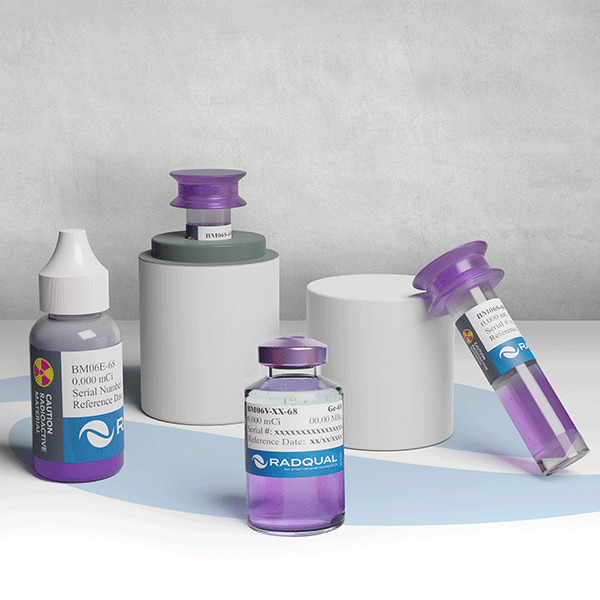
The Dual Geometry “S” vial standard is the only direct NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) traceable dose calibrator standard for Ga-68 and F-18 available. The patented design provides you with the capability of calibration in the traditional vial or in the needed syringe position for your dose calibrator. Both the 0.5 millicuries (18.5 MBq) and 1.0 millicurie (37 MBq) standards contains Ge-68, with Ga-68 in secular equilibrium, and is sent with a calibration certificate and custom decay calendar. Independent studies at 17 major PET facilities worldwide involving over 100 different ion chambers have shown that ALL were incorrect in assaying Ga-68 and F-18 using manufacturing preset nuclide values on the ion chamber.
- Available is S, E & V dose calibrator vial configurations.
- Dose calibrator standards are calibrated for Ge-68 activity against a traceable National Institute of Standards (NIST) source, using a pressurized ion chamber and cross calibrated for F-18 and Cu-64 calibration.
- All sources are shipped with a certificate of calibration, leak test certification, radiation safety and handling instructions and a custom decay calendar showing both the F-18 and Cu-64 equivalent activity.
- Each source is packaged in an individual lead shield.
| Model No. | Source Type | Nuclide | Activity |
|---|---|---|---|
| BM06S-6805 | S-Vial | Ge-68 | 0.5 mCi |
| BM06S-681 | S-Vial | Ge-68 | 1.0 mCi |
| BM06S-681XS | S-Vial | Ge-68 | 1.0 mCi w/extra shielding |
| BM06E-68 | E-Vial | Ge-68 | 0.5 or 1.0 mCi |
| BM06V-XX-68 | V-Vial | Ge-68 | 0.5 or 1.0 mCi |
| BM08-68 | Rod | Ge-68 | 0.1 µCi - 0.3 µCi |
